Molecular Fragment Screening Identifies Potential SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors
04/14/2021
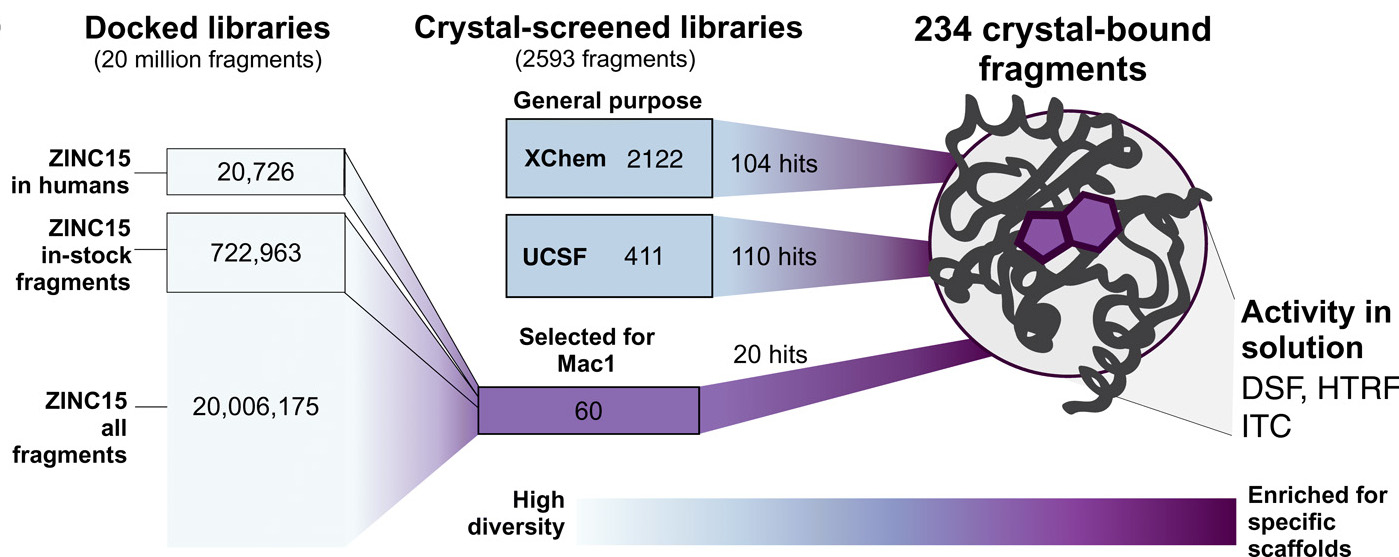
Overview of inhibitor fragment discovery for SARS-CoV-2. X-ray macromolecular crystallography and computational molecular docking were used to screen three libraries for unique fragments capable of binding to, and potentially inhibiting, the SARS-CoV-2 macrodomain (Mac1). Of the 20 million fragments screened, 234 were validated by isothermal titration calorimetry (ITC), differential scanning fluorimetry (DSF), and an HTRF-based ADPr-peptide displacement assay. [Reprinted under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International (CC BY 4.0) license from Schuller M. et al.2021. "Fragment binding to the Nsp3 macrodomain of SARS-CoV-2 identified through crystallographic screening and computational docking." Science Advances 7(16), eabf8711. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.abf8711.]
Research published in Science Advances provides a template for developing direct-acting antiviral drugs, with novel modes of action, to combat COVID-19 by suppressing the SARS-CoV-2 viral infection.

Surface representation of a SARS-CoV-2 macrodomain (Nsp3 Mac1) bound to the host signaling molecule ADPr (cyan), which inhibits the host immune response. [Credit: M. Schuller, et al. 2021. DOI:10.1126/sciadv.abf8711]
A large-scale crystallographic screening effort combined with computational docking identified 234 new molecules capable of targeting the active site of Mac1. These fragment structures provide starting points for developing potent SARS-CoV-2 Mac1 inhibitors.
Related Links
- Feature Story: Massive Fragment Screen Points to New SARS-CoV-2 Inhibitors
- BER Resource: Center for BioMolecular Structure
- BER Resource: Structurally Integrated Biology for the Life Sciences
- BER Resource: Structural Molecular Biology Resource
References
M. Schuller, G. J. Correy, S. Gahbauer, D. Fearon, T. Wu, R. E. Díaz, et al. “Fragment binding to the Nsp3 macrodomain of SARS-CoV-2 identified through crystallographic screening and computational docking.” Science Advances (2021) Vol. 7, Issue 16, Pages eabf8711. [DOI: 10.1126/sciadv.abf8711]
